Software Quality Assurance is a term that covers all aspects of guaranteeing a high-quality software product. It includes creating processes for each stage of development to reduce bugs and flaws during the build. Companies need it to measure the quality of the software.
At the heart of the QA process is software testing.
Software testing is the process of checking whether the software conforms to the requirements and works as expected.
Software testing aims to find the bugs (or defects) in the software and to report them for fixing.
Software testing can be manual or automated.
Manual testing is done by hand.
The QA engineer clicks on the software UI, fill and submits forms, interacts with the software UI, invokes back-end operations by hand or by specialized tools, executes certain functionality, validates that it works correctly, and tries to find defects.
Manual testing also involves testing the user experience (UX), the user interface, and the visual look and feel of the software.
Automated testing is done by scripts and programs, which perform robotic checks of the software.
Instead of clicking at the UI controls, filling and submitting forms by hand,
QA automation engineers record scripts and write programs to do automate this and to check whether the software behaves correctly without human innervation.
In addition to testing, there are a few other approaches to software quality assurance.
Code reviews and quality inspections are proactive approaches to software quality.
They aim to catch defects and bad practices early before they appear in the functionality.
Such practices are typically done by senior developers or senior QA engineers.
Code reviews aim to enforce good practices for internal code quality, such as writing understandable and maintainable code, avoiding repeating code, using clear abstractions, formatting the code correctly, naming identifiers correctly, structuring the code in a clear way, and many others.
Quality inspections try to find problems in the code, by understanding its program logic and internal design.
The goal of the testing process is to find and report the defects and issues with the software.
Reported bugs are described, submitted, and tracked in issue tracking software (or simply, bug tracker).
In the issue tracker, developers and QA engineers discuss the issues, prioritize them, assign them to team members, track the work on the issues and the changes of their status, confirm when an issue is fixed, and finally close it.
Issue trackers track not only the defects but also new feature requests and other issues with the software.
Software quality assurance is a broad topic in software engineering and is a separate profession in many software companies.
QA engineers should have basic software development and technical skills
and strong attention to the details and quality, to be diligent and patient, and to work persistently on the software quality, testing, and test automation.
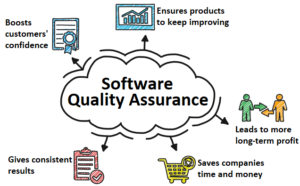
Here are some reasons for using Software Quality Assurance:
- Ensures products keep improving
 The Software Quality Assurance process is all about consistently maintaining high standards. Many of those standards depend on what customers want. As customers engage with a product, they will have suggestions on how to improve them.
The Software Quality Assurance process is all about consistently maintaining high standards. Many of those standards depend on what customers want. As customers engage with a product, they will have suggestions on how to improve them.
- Leads to more long-term profit
 Software Quality Assurance can boost profit in a few ways. The first is through saving more money by not wasting time and resources. The second is that the quality makes companies more competitive in the marketplace. Customers are willing to pay more for better quality.
Software Quality Assurance can boost profit in a few ways. The first is through saving more money by not wasting time and resources. The second is that the quality makes companies more competitive in the marketplace. Customers are willing to pay more for better quality.
- Saves companies time and money
 While it takes time at the beginning of the process to create systems that catch errors, it takes more time to fix the errors if they’re allowed to happen or get out of control. Paying to prevent problems is cheaper than paying to fix them.
While it takes time at the beginning of the process to create systems that catch errors, it takes more time to fix the errors if they’re allowed to happen or get out of control. Paying to prevent problems is cheaper than paying to fix them.
- Boosts customers’ confidence
 People will want to spend money on products, but only if they believe they’re getting something that’s worth the price. When businesses use Software QA processes, they’re letting customers know that they care about them and their priorities.
People will want to spend money on products, but only if they believe they’re getting something that’s worth the price. When businesses use Software QA processes, they’re letting customers know that they care about them and their priorities.
- Gives consistent results
 With software products, consistency is the most important factor for Software Quality Assurance. The QA ensures every product bearing the company’s name is the same. No customer is going to get something worse or better than another customer.
With software products, consistency is the most important factor for Software Quality Assurance. The QA ensures every product bearing the company’s name is the same. No customer is going to get something worse or better than another customer.
Software Quality Assurance is a must in Software Development as it ensures your software is built efficiently and is finished with minimal flaws and bugs. Without it, Software Development could be quite unreliable, with products potentially requiring complete do-overs.
Lesson Topics
- Software Quality Assurance
- Live Demo of Issue Tracker



